Honorable Mention
Dynamic Color Assignment for Hierarchical Data
Jiashu Chen - Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Weikai Yang - Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Zelin Jia - Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Lanxi Xiao - Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Shixia Liu - Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Download preprint PDF
Download Supplemental Material
Room: Bayshore II
2024-10-16T18:09:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-16T18:09:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
Color assignment, Hierarchical Visualization, Discriminability, Harmony.
Abstract
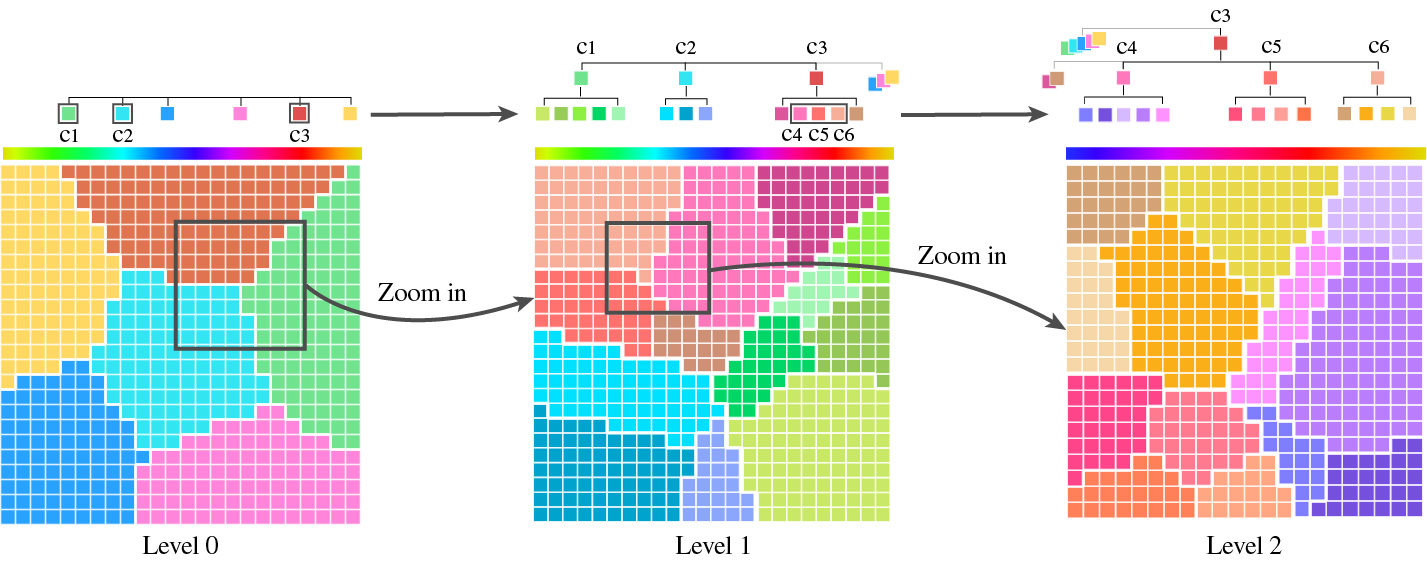
Assigning discriminable and harmonic colors to samples according to their class labels and spatial distribution can generate attractive visualizations and facilitate data exploration. However, as the number of classes increases, it is challenging to generate a high-quality color assignment result that accommodates all classes simultaneously. A practical solution is to organize classes into a hierarchy and then dynamically assign colors during exploration. However, existing color assignment methods fall short in generating high-quality color assignment results and dynamically aligning them with hierarchical structures. To address this issue, we develop a dynamic color assignment method for hierarchical data, which is formulated as a multi-objective optimization problem. This method simultaneously considers color discriminability, color harmony, and spatial distribution at each hierarchical level. By using the colors of parent classes to guide the color assignment of their child classes, our method further promotes both consistency and clarity across hierarchical levels. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in generating dynamic color assignment results with quantitative experiments and a user study.