Compress and Compare: Interactively Evaluating Efficiency and Behavior Across ML Model Compression Experiments
Angie Boggust - Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, United States
Venkatesh Sivaraman - Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, United States
Yannick Assogba - Apple, Cambridge, United States
Donghao Ren - Apple, Seattle, United States
Dominik Moritz - Apple, Pittsburgh, United States
Fred Hohman - Apple, Seattle, United States
Screen-reader Accessible PDF
Download preprint PDF
Download Supplemental Material
Room: Bayshore V
2024-10-17T13:18:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2024-10-17T13:18:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
Efficient machine learning, model compression, visual analytics, model comparison
Abstract
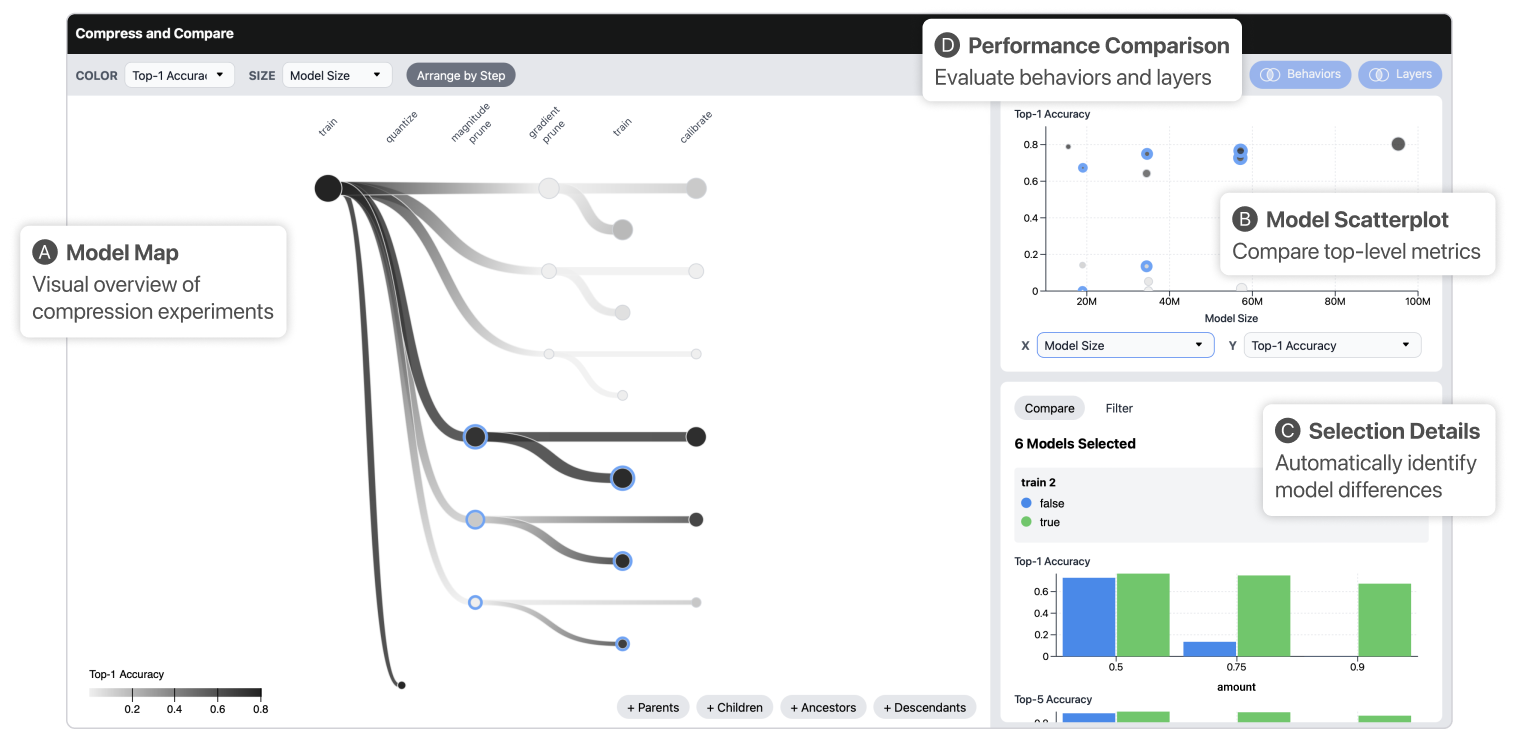
To deploy machine learning models on-device, practitioners use compression algorithms to shrink and speed up models while maintaining their high-quality output. A critical aspect of compression in practice is model comparison, including tracking many compression experiments, identifying subtle changes in model behavior, and negotiating complex accuracy-efficiency trade-offs. However, existing compression tools poorly support comparison, leading to tedious and, sometimes, incomplete analyses spread across disjoint tools. To support real-world comparative workflows, we develop an interactive visual system called Compress and Compare. Within a single interface, Compress and Compare surfaces promising compression strategies by visualizing provenance relationships between compressed models and reveals compression-induced behavior changes by comparing models’ predictions, weights, and activations. We demonstrate how Compress and Compare supports common compression analysis tasks through two case studies, debugging failed compression on generative language models and identifying compression artifacts in image classification models. We further evaluate Compress and Compare in a user study with eight compression experts, illustrating its potential to provide structure to compression workflows, help practitioners build intuition about compression, and encourage thorough analysis of compression’s effect on model behavior. Through these evaluations, we identify compression-specific challenges that future visual analytics tools should consider and Compress and Compare visualizations that may generalize to broader model comparison tasks.